What is the Network Definition?

Network Definition (GSM, CDMA, HSPA, EVDO, LTE and 5G)
A network definition refers to an interconnection system or communication system between two or more electronic devices.
To put it more simply, a network is an inter-communication system between multiple electronic devices that uses a communication system to send various files, data, messages, etc. from one computer to another.
What is the Network Definition?
A network definition refers to a facility that connects different devices and systems to exchange information and relationships between them. Networks connect each other through technology, so that information can be sent directly from one place to another.In today's time, everyone uses a network , be it mobile network or computer network. Without a network, we can easily talk to someone who is far away. You can share your photos, videos, etc. Sometimes the question comes to your mind: what is a network, what are the types of networks, what are the uses of networks and what are the advantages and disadvantages of networks. If similar questions come to your mind and you want to know their answers, then you have come to the right article.
Through today's article, we are going to tell you about networks in simple words, After reading this article, I hope you will not understand what a network is anymore. So without taking much of your time, let's start this article and learn what a network is.
Network definition
A network definition is a system of communication or information exchange between one or more computers or other electronic devices. Networks can be segmented in various ways, such as on the basis of ownership, size, technology, topology, protocol, etc. Here, I will tell you about some networks.
What is the computer network?
A computer network is a collection of multiple computers connected to each other through a communication system. Computers can exchange information, share files and programs, and communicate with each other through this communication system.
There are two types of networks based on ownership:
1. Public network
2. private network.
Public Network:
A public network is a network that is not owned by any particular person or organization and can be accessed by anyone at any time. For example, the Internet is the world's largest public network.
Private Network:
A private network is a network that is owned by a specific person or organization and is always controlled by that authority. For example, a network between computers in an office is called a private network.
Types of Computer Networks
Now let's know about the basic types of computer networks. There are five types of computer networks based on geographical location. namely-
PAN (Personal Area Network)
LAN (Local Area Network)
MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
CAN (Campus Area Network)
WAN (Wide Area Network)
There are 5 types of networks based on size: PAN, LAN, CAN, MAN, and WAN.
1. PAN (Personal Area Network):
It is a user's hobby—an internal network where the user's personal devices are connected. PAN stands for Personal Area Network, which is used to communicate between a person's own devices. An example of PAN is the communication of a Bluetooth headphone with a mobile phone.
2. LAN (Local Area Network):
It is a small area inside the company where devices are connected to the network. LAN stands for Local Area Network, which is used to communicate computers or other devices within a limited area. For example, the communication of a home computer, mobile device, printer, smart TV, etc. is an example of LAN.
3. MAN (Metropolitan Area Network):
It provides network connectivity between different locations in some areas of a large city. MAN stands for Metropolitan Area Network, which is used for the communication of computers or other devices within a city or metropolis. For example, the communication of various offices, banks, universities, government institutions, etc. in a city is an example of MAN.
4. CAN (Campus Area Network):
When the LAN network used in several buildings is connected to a single network to coordinate the work of different buildings at a university, the whole network is called CAN. This network was created to facilitate data transmission between multiple departments in universities, large offices, courts, and factories. Its coverage is up to 5 km. It is used for a large institution covering a large area.
5. WAN (Wide Area Network):
It is a large area where different LANs and other networks are connected. For example, the Internet can be a WAN. WAN stands for Wide Area Network, which is used to communicate computers or other devices within a country or world.
There are other different types of networks, such as:
WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network):
It connects different devices within one location where all the connections are.
VPN (Virtual Private Network):
It is a secure and private network that provides encrypted connections to public networks.
SAN (Storage Area Network):
It allows data and other resources between servers and storage devices or connects different storage between computer systems.
This type of network is designed for different stimuli and uses, providing the information needed for the service.
What are the advantages of using computer networks?
Computer networks have many advantages, including:
Remote access:
Using computer networks, users can access files and programs on remote computers.
Data Sharing:
Using computer networks, users can share files, programs, and other resources.
Communication:
Using computer networks, users can communicate with each other through email, text messages, and other communications.
Computer networks can be of various sizes, from small office networks to global networks. There are different types of computer networks, including:
Local Area Network (LAN):
A LAN is a computer network located in a small area, such as an office or a home.
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN):
A MAN is a computer network located in a large city or metropolitan area.
Wide Area Network (WAN):
A WAN is a computer network that spans a large area, such as a country or a continent.
Computer networks are built using different types of hardware and software. Hardware includes:
Computers:
Computers are members of the network.
Network Adapter:
Network adapters connect the computer to the network.
Network cables:
Network cables connect computers and network adapters.
Network hubs or switches:
Network hubs or switches connect computers to a network.
What are the types of network topology?
A computer network can have different topologies. Based on the commonly seen topologies, there are basically six types of network topologies. They are-
Star Topology
Ring Topology
Bus Topology
Tree Topology
Mesh Topology
Hybrid Topology
Differences between 2G, 3G, 4G, HSPA, LTE, EVDO, GPRS, and EDGE
Each successor to mobile network technology has a numerical number followed by the letter 'G', of the form 'vG'. So, 2G means second generation, 3G means third generation, 4G means fourth generation, etc. Each generation is more advanced than the previous one. Currently, 4G is the latest standard, but many major organizations have already started their work on the upcoming 5G wireless technology.
What are the functions and benefits of a network?
The main function of a network is to provide a single platform for participants to exchange data and share resources.
In an office, each workstation has its own computer. Without a network of computers, it would be very difficult for a team to work on a project because there would be no common place to share or store digital documents and information, and team members would not be able to share specific applications.
Without a network, it is not possible for the IT department to connect every computer to a printer.
The main advantages of the network are:
1. Share usage of data
2. Central control of programs and data
3. Central storage and data backup
4. Shared processing power and storage capacity
5. Easy management of approvals and responsibilities
The basic components of a computer network
From a broader lens, a computer network is made up of two basic blocks: nodes, or network devices, and links. Links connect two or more nodes to each other. The way these links carry information is defined by the communication protocol.
GSM Network vs CDMA Network
GSM and CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) are two popular radio standards used in the mobile world. Both technologies offer similar features but CDMA is more popular in the US than the rest of the world. Most countries in Europe and Asia use GSM networks. Some people may tell you that CDMA is better than GSM but this is not true
US operators moved to CDMA technology when GSM technology was in its infancy but now that GSM technology has caught up with CDMA, US operators do not feel the need to migrate to GSM technology. Most telecom companies in the rest of the world use GSM technology to run their networks and do not feel the need to migrate to CDMA technology.
GSM
GSM, short for Global System for Mobile Communications, is a mobile network standard with worldwide support for mobile phones. This standard was developed by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) to replace the first-generation (1G) analog telecommunications standard.
GSM serves as the first second-generation (2G) telecommunications standard with support for digital devices, unlike 1G cellular networks. It was first introduced in Finland and Europe in 1991. Currently, the GSM standard is owned by the GSM Association and is used worldwide, except in Japan and South Korea.
GSM phones focused on voice data transmission, but over time, GPRS (in 2000) and EDGE (in 2003) came into the picture to expand their capabilities to packet data transport, which brought Internet access. The bands used in most countries are the 850MHz and 1800MHz bands.
CDMA (Code-Division Multiple Access)
This type of network opens the door to multiple radio technologies. Its operation style is known as the multiple access method. Basically, CDMA consists of CDMAOne, CDMA2000, and W-CDMA. CDMAOne is also referred to as IS95, which is a second-generation network standard. Both CDMA2000 and W-CDMA (wideband CDMA) are based on third-generation (3G) technology.
With 3G standards (Voice over Internet Protocol), cellular calls, text, and MMS services, high data speeds and streaming are improved. Smartphones with 3G networks such as CDMA2000 and W-CDMA perform better than 2G standards in terms of Internet access and voice calls.
ISM
ISM is an industrial, scientific, and medical radio band reserved for medical, scientific, and industrial use. This band of radio frequencies is used in industrial, scientific and medical ISM machines.
HSPA (High Speed Packet Access)
HSPA is composed of HSDPA and HSUPA. HSDPA stands for High-Speed Downlink Packet Access.
HSPA provides higher data transmission than CDMA technology.
Between HSDPA and HSUPA, the former is often mentioned in the mobile world because download speed is considered more important. HSDPA (also known as 3.5G or Turbo 3G) can download at 5.76Mbps–7.2Mbps. Its main 3G bands include 850MHz, 900MHz, 1700MHz, 1900MHz, and 2100MHz.
LTE (long-term evolution)
LTE is popularly called "4G LTE." Currently, it is the highest internet speed standard in the world. It boasts download speeds of around 150Mbps to 300Mbps.
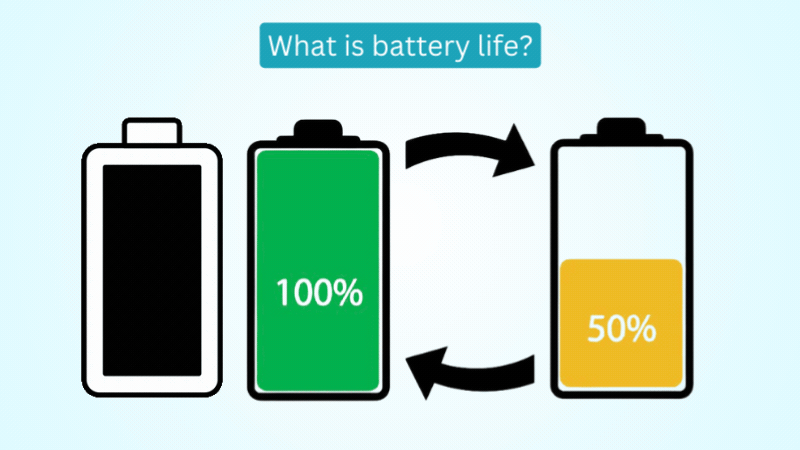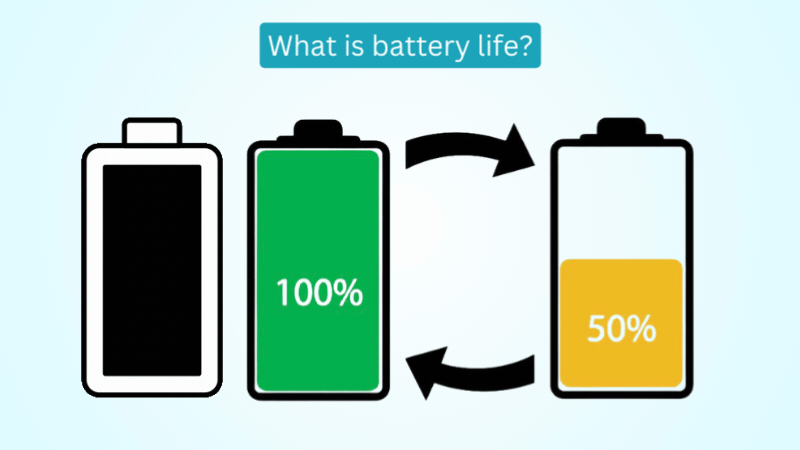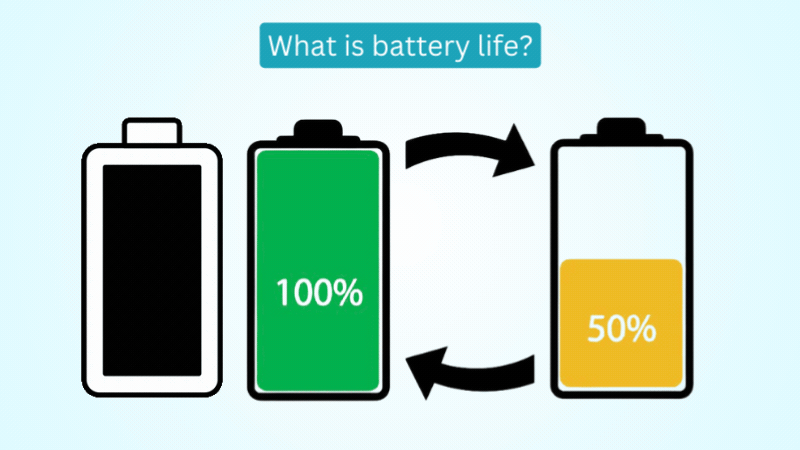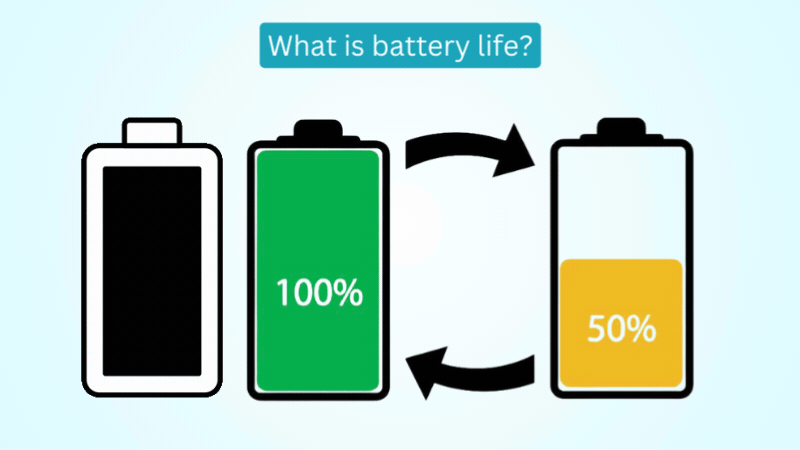
Compared to other networks, LTE places great demands on battery capacity. So, if you want to use the LTE standard extensively, you should be prepared to see higher battery consumption.
EVDO (Evolution-Data Optimized or Evolution-Data Only).
EVDO is a telecommunications standard for the transmission of data over radio signals, used for broadband Internet access. It uses multiplexing techniques, including code division multiple access (CDMA) as well as time division multiplexing (TDM), to maximize both individual user throughput and overall system throughput. It has been adopted by many mobile phone service providers around the world, especially those that previously employed CDMA networks. EVDO is designed as an evolution of the CDA2000 standard that will support higher data rates and a voice can be deployed.
Final thought:
A network is any interconnected system. Computer networking is the connection and interconnection of multiple computing devices, such as computers, servers, smartphones, and IoT devices, to share resources and information.
Network Definition: Related FAQs
1. What is a network definition?
Answer: A network definition refers to two or more computers connected to allow file exchange or electronic communication. Computers on a network may be connected by cables, telephone lines, radio waves, satellites, or infrared light beams.
2. What are the types of networks?
Answer: The two types of networks are local-area networks (LAN) and wide-area networks (WAN).
3. What are networks and the Internet?
Answer: A network is defined as a group of two or more computer systems. Whereas the Internet is the interconnection of several networks.
4. What does networking do?
Answer: Networking is the process of making connections and building relationships. A network definition refers to a facility that connects different devices and systems to exchange information and relationships between them. Networks connect each other through technology, so that information can be sent dire
ctly from one place to another